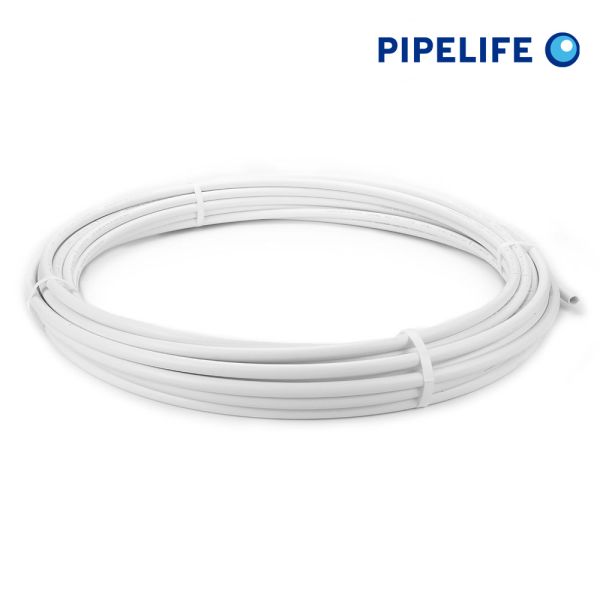
Pipelife PB Pipe Coils
Useful Information
What is PB Pipe Used For?
PB (Polybutylene) pipe coils are designed for plumbing applications in both residential and commercial settings. They are ideal for hot and cold water services, central and underfloor heating systems, providing a durable and efficient means of fluid and heat distribution.
Key Features
- Material: High-grade Polybutylene, offering excellent resistance to creep and environmental stress cracking.
- Corrosion Resistant: Not susceptible to corrosion or scale build-up.
- Low Noise Transmission: Due to their strength and wall thickness, they effectively reduce noise.
- Ultra-Flexible: Notably more flexible than other pipes, ensuring easy installation even in awkward spaces.
- Easy Handling: Soft material with little memory for a flexible and manageable pipe.
- Barrier Layer: 5-layer EVOH barrier, enhancing durability and performance.
- Compatibility: Works seamlessly with BS7291 specified systems.
- Approvals: Full BS7291-Class S and WRAS approvals, with a 50-year guarantee.
Specifications
- Material: Polybutylene (PB)
- Available Sizes: Metric sizes of 15mm, 22mm, and 28mm
- Colour: White
- Barrier Layer: 5-layer EVOH Barrier for enhanced performance
- Approvals: Fully compliant with BS7291-Class S and WRAS
- Guarantee: Comes with a 50-year guarantee
PB Pipe Dimensions
| Size (mm) | Outside Diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) |
| 15 | 15±0.1 | 1.5-1.8 |
| 22 | 22±0.1 | 2.0-2.3 |
| 28 | 28±0.1 | 2.6-2.9 |
Working Temperature & Pressure
| Application | Normal Working Temperature (°C) | Maximum Working Temperature (°C) | Maximum Working Pressure |
| Cold Water | 20 | 20 | 12 |
| Hot Water | 65 | 95 | 6 |
| Central Heating | 82 | 105 | 3 |
| Underfloor Heating | 35-55 | 60 | 3 |
Installation Instructions
- Cutting: Use a specific pipe cutter to ensure a clean, straight cut.
- Inserts: Use approved BS 7291 system pipe inserts before fitting to maintain pipe integrity.
- Bending: Utilize standard elbow fittings for sharp bends, and gentle bends can be achieved using pipe clips.
- Fittings: For push-fit or compression fittings, ensure the insert is placed before securing the fitting.
- Expansion and Contraction: Take into account the high coefficient of expansion for PB pipes during installation.
- Leak Testing: After installation, conduct a thorough leak test by gradually introducing water to the system.
- Final Checks: Ensure all connections are secure and the pipe layout allows for thermal expansion.
What is the Difference Between PB and PEX Pipe?
PEX (Crosslinked Polyethylene) and PB (Polybutylene) pipes are both popular for plumbing applications, but they have key differences:
- Material Properties: PB is known for its flexibility and resistance to environmental stress cracking, while PEX is recognized for its high temperature and pressure resistance.
- Installation: PB pipes are generally more flexible and easier to handle, making them preferable in tight and complex installations.
- Longevity and Durability: PEX typically offers greater long-term stability, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Application Suitability: While both are used in plumbing systems, PEX is often preferred for high-temperature applications due to its heat resistance.



